引言
二叉查找树是一种能将链表插入的灵活性和有序数组查找的高效性结合起来的一种重要的数据结构,它是我们后面学习红黑树和AVL树的基础,本文我们就先来看一下二叉查找树的实现原理。
二叉查找树的定义
二叉查找树最重要的一个特征就是:每个结点都含有一个Comparable的键及其相关联的值,该结点的键要大于左子树中所有结点的键,而小于右子树中所有结点的键。
下图就是一个典型的二叉查找树,我们以结点E为例,可以观察到,左子树中的所有结点A和C都要小于E,而右子树中所有的结点R和H都要大于结点E。
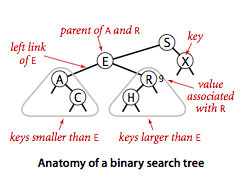
二叉查找树
在实现二叉查找树中相关操作之前我们先要来定义一个二叉查找树,由于Java中不支持指针操作,我们可以用内部类Node来替代以表示树中的结点,每个Node对象都含有一对键值(key和val),两条链接(left和right),和子节点计数器(size)。另外我们还提前实现了size(), isEmpty()和contains()这几个基础方法,三种分别用来计算二叉树中的结点数目,判断二叉树是否为空,判断二叉树中是否含有包含指定键的结点。
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private Node root; // root of BST
private class Node {
private Key key; // sorted by key
private Value val; // associated data
private Node left, right; // left and right subtrees
private int size; // number of nodes in subtree
public Node(Key key, Value val, int size) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.size = size;
}
}
// Returns the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table.
public int size() {
return size(root);
}
// Returns number of key-value pairs in BST rooted at x.
private int size(Node x) {
if(x == null) {
return 0;
} else {
return x.size;
}
}
// Returns true if this symbol table is empty.
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
// Returns true if this symbol table contains key and false otherwise.
public boolean contains(Key key) {
if(key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");
} else {
return get(key) != null;
}
}
}
|