Java 容器源码分析之 Deque 与 ArrayDeque(3)
|
 
- UID
- 1066743
|

Java 容器源码分析之 Deque 与 ArrayDeque(3)
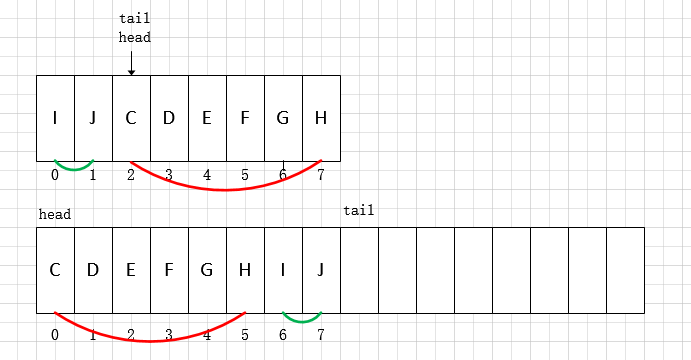
扩容在每次添加元素后,如果头索引和尾部索引相遇,则说明数组空间已满,需要进行扩容操作。 ArrayDeque 每次扩容都会在原有的容量上翻倍,这也是对容量必须是2的幂次方的保证。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| private void doubleCapacity() {
assert head == tail; //扩容时头部索引和尾部索引肯定相等
int p = head;
int n = elements.length;
//头部索引到数组末端(length-1处)共有多少元素
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
//容量翻倍
int newCapacity = n << 1;
//容量过大,溢出了
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
//分配新空间
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
//复制头部索引到数组末端的元素到新数组的头部
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
//复制其余元素
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
elements = a;
//重置头尾索引
head = 0;
tail = n;
}
|
移除元素ArrayDeque支持从头尾两端移除元素,remove方法是通过poll来实现的。因为是基于数组的,在了解了环的原理后这段代码就比较容易理解了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public E pollFirst() {
int h = head;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[h];
// Element is null if deque empty
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
return result;
}
public E pollLast() {
int t = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[t];
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[t] = null;
tail = t;
return result;
}
|
获取队头和队尾的元素1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E peekFirst() {
// elements[head] is null if deque empty
return (E) elements[head];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E peekLast() {
return (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
}
|
迭代器ArrayDeque 在迭代是检查并发修改并没有使用类似于 ArrayList 等容器中使用的 modCount,而是通过尾部索引的来确定的。具体参考 next 方法中的注释。但是这样不一定能保证检测到所有的并发修改情况,加入先移除了尾部元素,又添加了一个尾部元素,这种情况下迭代器是没法检测出来的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| private class DeqIterator implements Iterator<E> {
/**
* Index of element to be returned by subsequent call to next.
*/
private int cursor = head;
/**
* Tail recorded at construction (also in remove), to stop
* iterator and also to check for comodification.
*/
private int fence = tail;
/**
* Index of element returned by most recent call to next.
* Reset to -1 if element is deleted by a call to remove.
*/
private int lastRet = -1;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != fence;
}
public E next() {
if (cursor == fence)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[cursor];
// This check doesn't catch all possible comodifications,
// but does catch the ones that corrupt traversal
// 如果移除了尾部元素,会导致tail != fence
// 如果移除了头部元素,会导致 result == null
if (tail != fence || result == null)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
lastRet = cursor;
cursor = (cursor + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
return result;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (delete(lastRet)) { // if left-shifted, undo increment in next()
cursor = (cursor - 1) & (elements.length - 1);
fence = tail;
}
lastRet = -1;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
Object[] a = elements;
int m = a.length - 1, f = fence, i = cursor;
cursor = f;
while (i != f) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)a;
i = (i + 1) & m;
if (e == null)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
action.accept(e);
}
}
}
|
除了 DeqIterator,还有一个反向的迭代器 DescendingIterator,顺序和 DeqIterator 相反。 |
|
|
|
|
|

